Hussar
Hussar is a highly flexible Matlab framework for solving propagation problems.
The software is based on the mix of the Unidirectional Pulse Propagation Equation
approach and the "not necessarily slowly varying envelope" concept.
This composition enables an accurate modeling and small memory requirements.
Download Hussar here.
Versions
1.3 (2018.07.26) Current version with a few bug fixes and several new features. (manual for version 1.3)
.
1.2 (2018.04.21) Current version with a few bug fixes and several new features. (manual for version 1.2)
.
1.1 (2017.05.10) The approximated noncollinear propagation was removed from this version (manual for version 1.1)
.
1.0 (2016.06.28) Older version with approximated noncollinear propagation enabled (manual for version 1.0)
Support
Manual - basic informations on the software usage for version 1.3, for version 1.2, for version 1.1, for version 1.0
Class and Function Reference Manual - Definitions of the classes and functions for the Hussar library.
The manual is a work in progress particular parts of it are being completed on the user request, pleas don't hesitate to contact
or to use any of the following methods to contact the team and direct us to complete particular chapters.
Ultrafast Soft on Facebook - through our Facebook website one can track news, contact the team, report bugs and submit "user's wishes".
News Letter - through news letter we inform about new Hussar releases (we are keeping it brief and rare).
Go to download Hussar page to subscribe for news letter.
Mailing list - Users can contact development team and each other almost instantaneously through the mailing list.
One can subscribe via web page,
subscribe via email, or through download Hussar page.
Forum - Announcements, bug reporting and whish list can also be found on our forum.
On your laboratory PC
Hussar has been created for PC computers. 4GB RAM is enough for running simulations with 3 envelopes (SFG/DFG/OPA etc.) and 4 million points in the grid of each envelope (e.g grid of 128x128x256 points in 3D and 1024x4096 points in 2D simulation).
Availability
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

Features
Linear effects
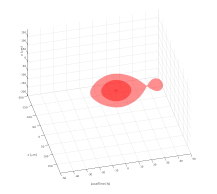
Linear pulse and beams propagation in birefringent media can easily be performed (in single step). All: 1+1D (T+Z), 2+1D (beam XY+Z, and pulses in cartesian TX+Z or cylindrical TR+Z coordinates) and 3+1D (TXY+Z) simulations can be performed. On the right a visualization of a Laguerre-Gaussian LP01 mode propagation in biaxial BiBO crystal is presented.
Three wave mixing
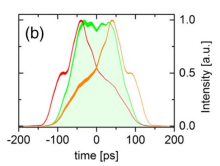
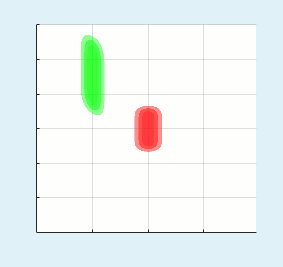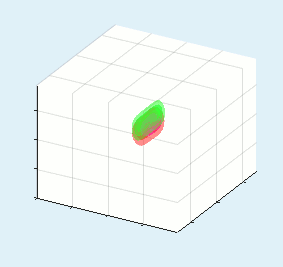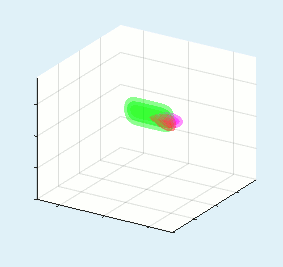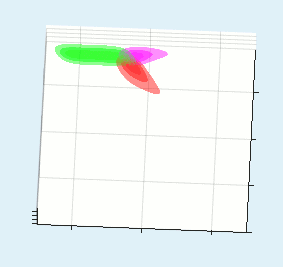
All three wave mixing phenomena: SHG, SFG, DFG, OPA, fluorescene up conversion, etc. can be simulated both in collinear and non-collinear configurations apart of 3+1D (TXY+Z) simulations for large beam sizes the fast 2+1D (TX+Z) simulation can be performed. An example of blue light pumped NOPA simulation is presented in the top of the page.
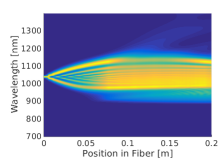
Supercontinuum generation
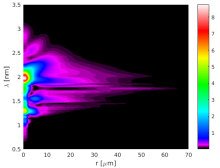
Supercontinuum generation in bulk materials is possible in 3+1D (TXY+Z) or 2+1D (TR+Z) cylindrical coordinates. Apart from SPM (= Self-Focusing), SRS, Self-Steepening and linear effects the photoionization (Multiphoton or Keldysh model) and current interaction (Drude model) can be included.
>